Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shobuda, Yoshihiro
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 27(1), p.011001_1 - 011001_25, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.44(Physics, Nuclear)When computing the space charge tune shift for a relativistic bunched beam within a cylindrical chamber, mirror currents for a coasting beam, initially introduced to replace the chamber wall, are employed. Subsequently, the obtained result is extended to encompass the bunched beam, taking into account the bunching factor which quantifies the distribution of bunches around the accelerator ring. In the process of derivation, the terms that characterize the bunch length are intuitively integrated into the formula. As a result, the validity of this approach has never been established. This study provides the derivation of the space charge tune shift formula for both relativistic and non-relativistic bunched beams right from the outset, employing the Green function formalism. Subsequently, it is compared with the earlier formula derived using mirror currents.
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Togashi, Tomohito; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamamoto, Masanobu
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 26(5), p.053501_1 - 053501_45, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)At the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) in Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), theoretical predictions have indicated that the kicker-impedance would excite the beam-instability. A 1 MW beam with large emittance can be delivered to the Material and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) through suppression of the beam instabilities by choosing the appropriate machine parameters. However, we require other high-intensity and high-quality smaller emittance beams (than the 1 MW beam) for the Main Ring (MR). Hence, we proposed a scheme for suppressing the kicker-impedance by using prototype diodes and resistors, thereby demonstrating the effect on the kicker impedance reduction. However, the J-PARC RCS must be operated with a repetition rate of 25 Hz, which urged us to consider special diodes that are tolerant to heating. After developments, we have demonstrated that the special diodes with resistors can suppress the beam instability by reducing the kicker impedance. Enhanced durability of the prototype diodes and resistors for the 25 Hz operation was also realized. Moreover, the new diodes and the resistors have negligible effect on the extracted beam from the RCS. From a simulation point of view, the scheme can be employed for at least 5 MW beam operation within the stipulated specifications.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 26(3), p.032802_1 - 032802_12, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is a useful device for performing longitudinal beam tuning using the pointwise longitudinal phase distribution measured at selected points in the beam transportation. To measure the longitudinal phase distribution of a low-energy negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H
) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
Yee-Rendon, B.; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Nakano, Keita; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 25(8), p.080101_1 - 080101_17, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear)High reliability and availability are primary goals for the operation of particle accelerators, especially for accelerator-driven subcritical systems (ADS). ADSs employ high-power beams for the transmutation of minor actinide; as a result, the amount and the radiotoxicity of the nuclear waste are considerably reduced. To this end, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency is designing a 30-MW continuous wave (cw) super-conducting proton linear accelerator (linac) that supplies neutrons to an 800-MW subcritical reactor by a spallation process. The major challenge for an ADS linac is the strict control of the beam trip duration and its frequency to avoid thermal stress in the subcritical reactor structures. The maximum allowed beam trips for failures longer than a few seconds are estimated to be far below the rate achieved in current accelerators. Thus, we implemented a combination of hot standby and local compensation that enables a fast beam recovery. This work comprehensively investigated the tolerance of our linac lattice for the local compensations for failures in superconducting cavities and magnets. This scheme includes simultaneous compensation of multiple cavities in independent and same cryomodules that significantly enhance the reliability of the linac. The returned schemes present acceptable beam performance to guarantee the integrity of the linac and the beam transport to the target; moreover, they satisfy the beam stability in the beam window. In addition, the readjusted elements are subjected to moderate stress to ensure a sustainable operation. This manuscript reports the beam dynamics results toward fulfilling the high reliability demanded by an ADS linac.
Yee-Rendon, B.; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Tamura, Jun
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 24(12), p.120101_1 - 120101_17, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:46.8(Physics, Nuclear)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is working on the research and development of a 30-MW continuous wave (CW) proton linear accelerator (linac) for the JAEA accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS) proposal. The linac will accelerate a 20 mA proton beam to 1.5 GeV, using mainly superconducting cavities. The main challenge for an ADS accelerator is the high reliability required to prevent thermal stress in the subcritical reactor; thus, we pursue a robust lattice to achieve stable operation. To this end, the beam optics design reduces the emittance growth and the beam halo through the superconducting part of the linac. First, we simulated an ideal machine without any errors to establish the operation conditions of the beam. Second, we applied element errors and input beam errors to estimate the tolerance of the linac design. Finally, we implemented a correction scheme to increase the lattice tolerance by reducing the beam centroid offset on the transverse plane. Massive multiparticle simulations and a cumulative statistic of 1 10
10 macroparticles have shown that the JAEA-ADS linac can operate with less than 1 W/m beam losses in error scenarios.
macroparticles have shown that the JAEA-ADS linac can operate with less than 1 W/m beam losses in error scenarios.
Kamiya, Junichiro; Kotoku, Hirofumi*; Kurosawa, Shunta*; Takano, Kazuhiro; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Wada, Kaoru
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 24(8), p.083201_1 - 083201_23, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)Through the operation of the vacuum system in J-PARC, it becomes evident that the high-power beam has more powerful effects on the vacuum system than expected. Those effects are the malfunction of vacuum equipment and the large pressure rise. The former is the failure of the turbomolecular pump (TMP) controller. The TMP itself is also damaged by a bearing crush due to a touch-down. We have developed a TMP controller that can connect with long cables of more than 200 m lengths to install the controller in a control room where there is no radiation influence. The TMP with high-strength bearing has been also developed. The latter is an extreme pressure rise with increasing the beam power. It is indicated that the pressure rise mechanism is a result of ion-stimulated gas desorption. It is finally confirmed that the dynamic pressure during the high-power beam is effectually suppressed by additionally installing the NEG pumps.
Yamada, Ippei; Wada, Motoi*; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 24(4), p.042801_1 - 042801_13, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:46.8(Physics, Nuclear)A transverse beam profile monitor that visualizes a two-dimensional beam-induced fluorescent image was developed. The monitor employs a sheet-shaped gas flow formed by a technique of rarefied gas dynamics. A simplified analysis method was developed to reconstruct the beam intensity profile from the obtained image. The developed profile monitor and the analysis method were applied to measure the J-PARC 3 MeV H beam profile. The root mean square values of the profiles were consistent with the ones obtained by a wire-scanning-type beam profile monitor. The beam loss due to the gas sheet injection was measured as a beam-current reduction. The amount of the beam current decreased in proportion to the gas sheet flux and the reduction ranged from 0.004 to 2.5%. The assembled system was capable of reconstructing a beam profile from a single shot beam pulse (1.7
beam profile. The root mean square values of the profiles were consistent with the ones obtained by a wire-scanning-type beam profile monitor. The beam loss due to the gas sheet injection was measured as a beam-current reduction. The amount of the beam current decreased in proportion to the gas sheet flux and the reduction ranged from 0.004 to 2.5%. The assembled system was capable of reconstructing a beam profile from a single shot beam pulse (1.7 10
10 protons in 50
protons in 50  s).
s).
Kitamura, Ryo; Bae, S.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kim, B.*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Mibe, Tsutomu*; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 24(3), p.033403_1 - 033403_9, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.91(Physics, Nuclear)A negative muonium ion (Mu ) source using an aluminum foil target was developed as a low-energy muon source. An experiment to produce Mu
) source using an aluminum foil target was developed as a low-energy muon source. An experiment to produce Mu ions was conducted to evaluate the performance of the Mu
ions was conducted to evaluate the performance of the Mu ion source. The measured event rate of Mu
ion source. The measured event rate of Mu ions was
ions was 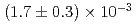 Mu
Mu /s when the event rate of the incident muon beam was
/s when the event rate of the incident muon beam was 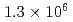 /s. The formation probability, defined as the ratio of the Mu
/s. The formation probability, defined as the ratio of the Mu ions to the incident muons on the Al target, was
ions to the incident muons on the Al target, was 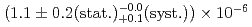 . This Mu
. This Mu ion source boosted the development of the muon accelerator, and the practicality of this low-energy muon source obtained using a relatively simple apparatus was demonstrated.
ion source boosted the development of the muon accelerator, and the practicality of this low-energy muon source obtained using a relatively simple apparatus was demonstrated.
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Toyama, Takeshi*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(9), p.092801_1 - 092801_18, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.56(Physics, Nuclear)The beam impedance of a ceramic break with titanium nitride (TiN) coating consists of three electric components in parallel: resistive wall term caused by TiN, radiation term, and capacitive term made by the ceramic itself. The entire wall current continues to run in the thin TiN even when the skin depth is much larger than the chamber thickness, except for the extremely thin TiN satisfying the condition that the radiation loss from the ceramic break becomes lower than the energy loss due to the DC-current on the thin TiN. This characteristic is useful in developing a wall current monitor with an improved frequency response. This study demonstrates the feature of the "ceramic break" monitor up to a few GHz from the theoretical and measurement points of view.
Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(8), p.082801_1 - 082801_13, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.12(Physics, Nuclear)Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Fujimori, Hiroshi*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(6), p.062802_1 - 062802_24, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:36.4(Physics, Nuclear)As hadron accelerators for such as the ADS and spallation neutron source achieve increasing beam power, damage to targets is becoming increasingly severe. To mitigate this damage, nonlinear beam optics based on octupole magnets is attractive. Nonlinear optics can decrease the beam-focusing hazard due to failure of the rastering magnet. As a side effect of nonlinear optics, the beam size is known to expand drastically compared with linear optics. Nonlinear effects have been studied via a simplified filament model that ignores beam-divergence spread at the octupole magnet. In this study, a new generalized model is proposed for application to an octupole magnet, regardless of the filament-model approximation. It is found that the transverse distribution obtained by beam tracking can be specified by the introduction of only two parameters, namely the normalized octupole strength of 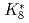 and the
and the 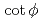 of the phase advance. To achieve the two antagonistic requirements of reduction of the beam-peak density and minimization of the beam loss, the transverse distribution is surveyed for a large range of beam position. It is found that a bell-shaped distribution with
of the phase advance. To achieve the two antagonistic requirements of reduction of the beam-peak density and minimization of the beam loss, the transverse distribution is surveyed for a large range of beam position. It is found that a bell-shaped distribution with 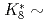 1 and
1 and 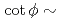 3 can satisfy requirements. This result is applied to beam transport in the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. The calculation result given by the present model shows good agreement with the experimental data, and the peak current density is reduced by 50% compared with the linear-optics case.
3 can satisfy requirements. This result is applied to beam transport in the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. The calculation result given by the present model shows good agreement with the experimental data, and the peak current density is reduced by 50% compared with the linear-optics case.
Hotchi, Hideaki
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(5), p.050401_1 - 050401_13, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.56(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.94(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Jameson, R. A.*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 22(12), p.120101_1 - 120101_8, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:64.15(Physics, Nuclear)Radio frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ) is the key component which realized modern high-current proton linacs, however, many RFQs are designed based on very conventional design schemes. We developed 3-MeV 50-mA H (negative hydrogen) RFQ based on a beam space-charge physics concept. The equipartitioning scheme, which is widely used in the high intensity linac design, is implemented into the RFQ design. Design performances of 99.1% transmission, 0.24
(negative hydrogen) RFQ based on a beam space-charge physics concept. The equipartitioning scheme, which is widely used in the high intensity linac design, is implemented into the RFQ design. Design performances of 99.1% transmission, 0.24 mm mrad transverse normalized rms emittance, and 0.11
mm mrad transverse normalized rms emittance, and 0.11 MeV deg for longitudinal direction are achieved with a vane length of 3 m and the final energy of 3 MeV. An RFQ employing this design concept was fabricated, and the design performance was confirmed by beam commissioning. In this paper, the design and result of the beam commissioning of this fully equipartitioned RFQ are described.
MeV deg for longitudinal direction are achieved with a vane length of 3 m and the final energy of 3 MeV. An RFQ employing this design concept was fabricated, and the design performance was confirmed by beam commissioning. In this paper, the design and result of the beam commissioning of this fully equipartitioned RFQ are described.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Omori, Chihiro*; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*; Furusawa, Masashi*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 22(9), p.092001_1 - 092001_22, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:47.88(Physics, Nuclear)Beam loading compensation in the rf cavities is a key for acceleration of high intensity beams in 3 GeV RCS of the J-PARC. Since we employ wideband magnetic alloy rf cavities for the J-PARC RCS and the wake voltage contains several harmonics, a multiharmonic beam loading compensation is required. The multiharmonic rf feedforward for the most important six harmonics is implemented in the existing low level rf (LLRF) control system, which has been working fairly well for acceleration of high intensity beams of up to 1 MW. However, we found the degradation of the performance for compensation of the feedforward with very high intensity beams. Therefore, a multiharmonic vector rf voltage control has been developed. The detail of system configuration, commissioning methodology, and beam test results using very high intensity beams are described. The beam loading by the 1 MW equivalent beam in the cavity is successfully compensated.
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Chin, Y. H.*; Hayashi, Naoki; Irie, Yoshiro*; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Togashi, Tomohito; Toyama, Takeshi*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamamoto, Masanobu
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 21(6), p.061003_1 - 161003_15, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.29(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Bae, S.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 21(5), p.050101_1 - 050101_6, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.82(Physics, Nuclear)Muons have been accelerated by using a radio-frequency accelerator for the first time. Negative muonium atoms (Mu ), which are bound states of positive muons and two electrons, are generated from through the electron capture process in an aluminum degrader. The generated Mu
), which are bound states of positive muons and two electrons, are generated from through the electron capture process in an aluminum degrader. The generated Mu 's are initially electrostatically accelerated and injected into a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). In the RFQ, the Mu
's are initially electrostatically accelerated and injected into a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). In the RFQ, the Mu 's are accelerated to 89 keV. The accelerated Mu
's are accelerated to 89 keV. The accelerated Mu 's are identified by momentum measurement and time of flight. This compact muon linac opens the door to various muon accelerator applications including particle physics measurements and the construction of a transmission muon microscope.
's are identified by momentum measurement and time of flight. This compact muon linac opens the door to various muon accelerator applications including particle physics measurements and the construction of a transmission muon microscope.
Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hayashi, Naoki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Tamura, Fumihiko; Tani, Norio; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 21(2), p.024203_1 - 024203_20, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:65.56(Physics, Nuclear)Chin, Y. H.*; Chao, A. W.*; Blaskiewicz, M. M.*; Shobuda, Yoshihiro
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 20(7), p.071003_1 - 071003_18, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.84(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hayashi, Naoki; Kato, Shinichi; Kinsho, Michikazu; Okabe, Kota; Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Tani, Norio; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 20(6), p.060402_1 - 060402_25, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:88.02(Physics, Nuclear)The 3-GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) is the world's highest class of high-power pulsed proton driver, aiming for an output beam power of 1 MW. The most important issues in realizing such a high-power beam operation are to control and minimize beam loss for maintaining machine activations within permissible levels. In RCS, numerical simulation was successfully utilized along with experimental approaches to isolate the mechanism of beam loss and find its solution. By iteratively performing actual beam experiments and numerical simulations, and also by several hardware improvements, we have recently established a 1-MW beam operation with very low fractional beam loss of a couple of 10 . In this paper, our recent efforts toward realizing such a low-loss high-intensity beam acceleration are presented.
. In this paper, our recent efforts toward realizing such a low-loss high-intensity beam acceleration are presented.